结合MDN食用
HTML 常见元素 文本 1 2 3 4 5 6 <h1 > 1号标题</h1 > <h2 > 2号标题</h2 > <h3 > 3号标题</h3 > <h4 > 4号标题</h4 > <h5 > 5号标题</h5 > <h6 > 6号标题</h6 >
段落 无序列表-ul 1 2 3 4 5 <ul > <li > 列表项1</li > <li > 列表项2</li > <li > 列表项3</li > </ul >
有序列表-ol 1 2 3 4 5 <ol > <li > 列表项1</li > <li > 列表项2</li > <li > 列表项3</li > </ol >
多级列表-嵌套使用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 <ul > <li > 北京市 <ul > <li > 海淀区</li > <li > 朝阳区</li > <li > 昌平区</li > </ul > </li > <li > 河北省 <ul > <li > 石家庄</li > <li > 保定</li > </ul > </li > </ul >
超链接 1 <a href ="网页地址" > 超链接文本</a >
多媒体 image Video 1 <video src ="文件路径" > </video >
Audio 1 <audio src ="文件路径" > </audio >
表单 表单的作用:收集用户填入的数据,并将这些数据提交给服务器
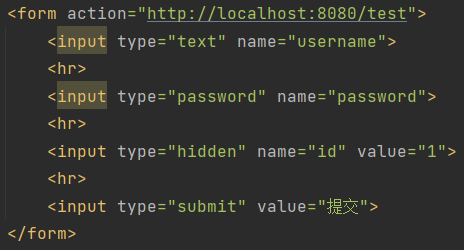
1 2 3 4 5 <form action ="服务器地址" method ="请求方式" enctype ="数据格式" > <input type ="submit" value ="提交按钮" > </form >
1 2 3 4 <form action ="https://www.baidu.com/s" > <input type ="text" name ="wd" > <input type ="submit" value ="搜索" > </form >
method 请求方式有
get (默认)提交时,数据跟在 URL 地址之后
post 提交时,数据在请求体内
enctype 在 post 请求时,指定请求体的数据格式
application/x-www-form-urlencoded(默认)
multipart/form-data
其中表单项提供多种收集数据的方式
有 name 属性的表单项数据,才会被发送给服务器
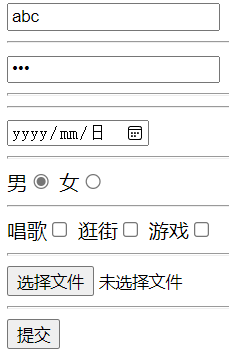
常见的表单项 文本框
1 <input type ="text" name ="uesrname" >
密码框
1 <input type ="password" name ="password" >
隐藏框
1 <input type ="hidden" name ="id" >
日期框
1 <input type ="date" name ="birthday" >
单选
1 2 <input type ="radio" name ="sex" value ="男" checked > <input type ="radio" name ="sex" value ="女" >
多选
1 2 3 <input type ="checkbox" name ="fav" value ="唱歌" > <input type ="checkbox" name ="fav" value ="逛街" > <input type ="checkbox" name ="fav" value ="游戏" >
文件上传
1 <input type ="file" name ="avatar" >
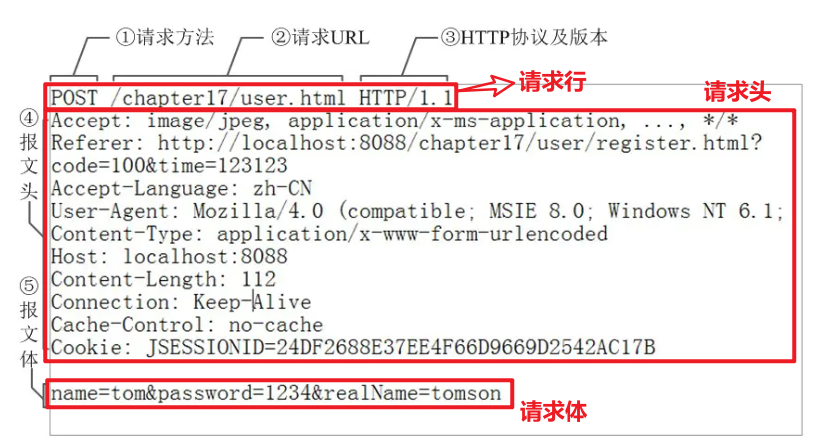
举例 HTTP请求 1、请求行 2、请求头 3、请求体
get 请求示例 1 2 GET /test2?name=%E5%BC%A0&age=20 HTTP/1.1 Host: localhost
%E5%BC%A0 是【张】经过 URL 编码后的结果
post 请求示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 POST /test2 HTTP/1.1 Host: localhost Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Content-Length: 21 name=%E5%BC%A0&age=18
application/x-www-form-urlencoed 格式细节:
参数分成名字和值,中间用 = 分隔 多个参数使用 & 进行分隔 【张】等特殊字符需要用 encodeURIComponent() 编码为 【%E5%BC%A0】后才能发送
json 请求示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 POST /test3 HTTP/1.1 Host: localhost Content-Type: application/json Content-Length: 25 {"name":"zhang","age":18}
json对象格式为:{"属性名":属性值},属性值可以是字符串,数字,布尔类型,null
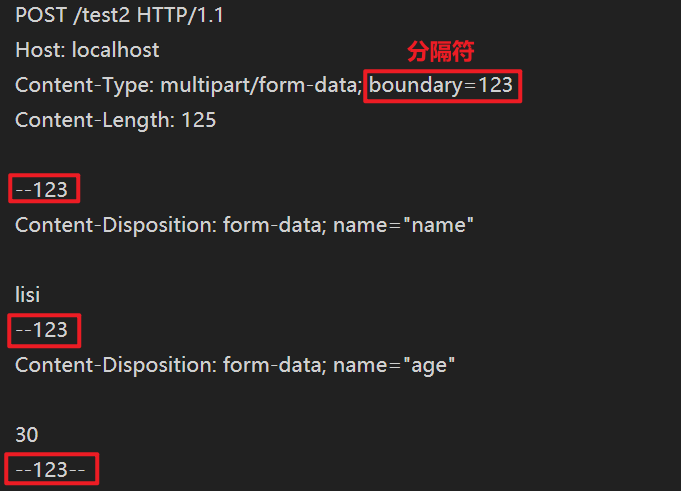
multipart 请求示例
boundary=123 用来定义分隔符
起始分隔符是 --分隔符
结束分隔符是 --分隔符--
数据格式小结 客户端发送
编码
application/x-www-form-urlencoded :url 编码
application/json:utf-8 编码
multipart/form-data:每部分编码可以不同
表单只支持以 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 和 multipart/form-data 格式发送数据 文件上传需要用 multipart/form-data 格式 js 代码可以支持任意格式发送数据
服务端接收
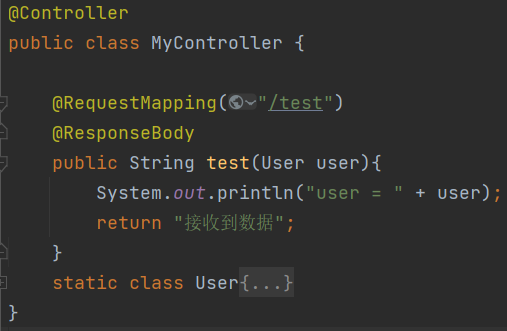
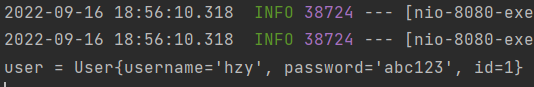
对 application/x-www-form-urlencoded 和 multipart/form-data 格式的数据,Spring 接收方式是统一的,只需要用 java bean 的属性名对应请求参数名即可 对于 applicaiton/json 格式的数据,Spring 接收需要使用 @RequestBody 注解 + java bean 的方式
CSS 选择器 type 选择器 - 根据标签名进行匹配(元素选择器)
class 选择器 - 根据元素的 class 属性进行匹配
id 选择器 - 根据元素的 id 属性进行匹配
属性和值
background-color : red;
…
display
布局 与布局相关的 html 元素
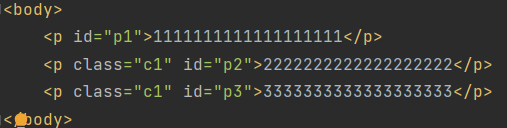
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 p { background-color :rgb (243 , 136 , 42 ); } .c1 { background-color : rgb (151 , 211 , 48 ); } #p3 { background-color : cyan; display : block; }
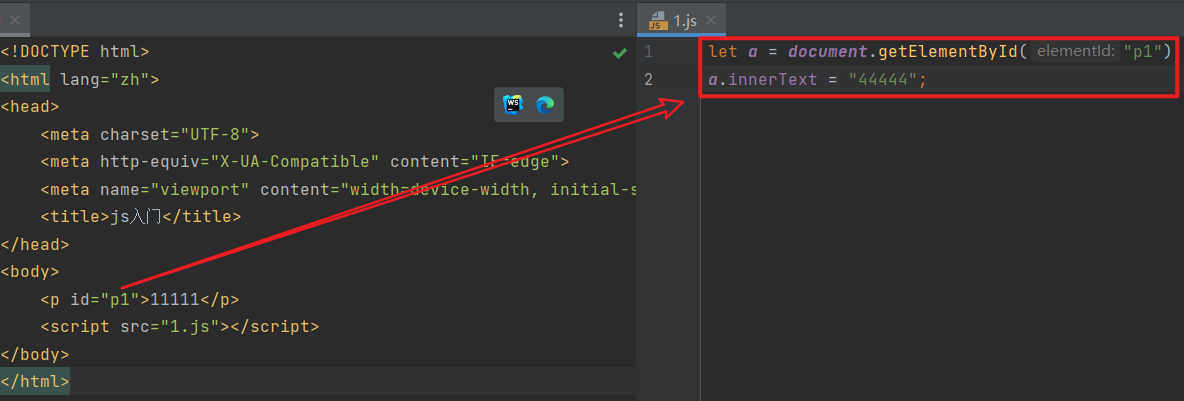
JS 示例:将11111修改为44444
js 代码位置
引入 js 脚本
1 <script src ="js脚本路径" > </script >
注意:到了框架之后,引入方式会有不同
声明变量 let let 声明的变量可以被多次赋值
const const 修饰的叫常量,只能赋值一次
1 2 const b = 300 ; b = 400 ;
const 并不意味着它引用的内容不可修改,例如:
1 2 3 const c = [1 ,2 ,3 ];c[2 ] = 4 ; c = [5 ,6 ];
var var 声明的变量可以被多次赋值,例如:
基本类型 undefined 和 null(*)
执行表达式或函数,没有返回结果,出现 undefined 访问数组不存在的元素,访问对象不存在的属性,出现 undefined 定义变量,没有初始化,出现 undefined
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 console .log (1 ); let a = 10 ; let b = [1 ,2 ,3 ];console .log (b[10 ]); let c = {"name" :"张三" };console .log (c.age ); let d;console .log (d);
二者共同点
二者区别
undefined 由 js 产生
null 由程序员提供
string js 字符串三种写法
1 2 3 let a = "hello" ; let b = "world" ; let c = `hello` ;
html 代码如下,用 js 中的字符串如何表示?
1 <a href ="1.html" > 超链接</a >
1 2 3 let s1 = '<a href="1.html">超链接</a>' ;let s2 = `<a href="1.html">超链接</a>` ;
模板字符串(Template strings)
需求:拼接 URI 的请求参数,如
1 2 /test?name=zhang&age=18 /test?name=li&age=20
传统方法拼接
1 2 3 4 let name = ; let age = ; let uri = "/test?name=" + name + "&age=" + age;
模板字符串方式
1 2 3 4 let name = ; let age = ; let uri = `/test?name=${name} &age=${age} ` ;
number 和 bigint number 类型标识的是双精度浮动小数,例如
既然是浮点小数,那么可以除零
浮点小数都有运算精度问题,例如
字符串转数字
1 2 3 4 5 parseInt ("10" ); parseInt ("10.5" ); parseInt ("10" ) / 3 ; parseInt ("abc" );
要表示真正的整数,需要用 bigint,数字的结尾用 n 表示它是一个 bigint 类型
boolean 在 js 中,并不是 boolean 才能用于条件判断,你可以在 if 语句中使用【数字】、【字符串】… 作为判断条件
1 2 3 4 5 let b = 1 ;if (b) { console .log ("进入了" ); }
这时就有一个规则,当需要条件判断时,这个值被当作 true 还是 false,当作 true 的值归类为 truthy,当作 false 的值归类为 falsy
下面值都是 falsy
falseNullish (null, undefined)0, 0n, NaN"" '' `` 即长度为零的字符串
剩余的值绝大部分都是 truthy
有几个容易被当作 falsy 实际是 truthy 的
"false", "0" 即字符串的 false 和 字符串的零[] 空数组{} 空对象
Function 定义 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 function 函数名(参数...) { return 结果; } function add (a,b ){ return a+b; }
调用函数 匿名函数 1 2 3 4 5 (function (参数 ) { return 结果; })
第一种使用场景:定义完毕后立刻调用:
1 2 3 (function (a,b ){ return a+b; })(1 , 2 )
第二种使用场景:作为其他对象的方法
页面存在元素
该元素有一个onclick方法,会在鼠标单机这个元素后被执行,onclick方法刚开始为null,需要赋值后才可以使用
1 2 3 document .getElementById ("p1" ).onclick = (function ( console .log ("鼠标进行单击..." ); });
箭头函数 1 2 3 4 (参数) => { return 结果; }
如果只有一个参数,则()可以省略
如果函数体内只有一行代码,{}可以省略
如果没有参数,() 还是要保留
1 document .getElementById ("p1" ).onclick = () => console .log ("aa" );
函数作为对象的情况 1、参与赋值,例如:具名函数也能参与赋值
1 2 3 4 function test ( console .log ("test" ); } document .getElementById ("p1" ).onclick = test;
2、作为方法参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 function a ( console .log ('a' ) } function b (fn ) { console .log ('b' ) fn (); } b (a);
3、作为方法返回值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function c ( console .log ("c" ); function d ( console .log ("d" ); } return d; } c ();c ()();
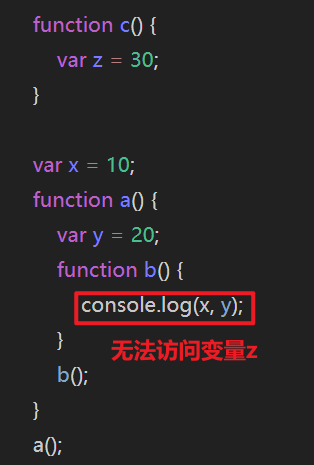
函数作用域 以函数为分界线划定作用域,所有函数之外是全局作用域
查找变量时,由内向外查找
在内层作用域找到变量,就会停止查找,不会再找外层 所有作用域都找不到变量,报错
闭包 其实就是指函数能够访问自己的作用域中变量
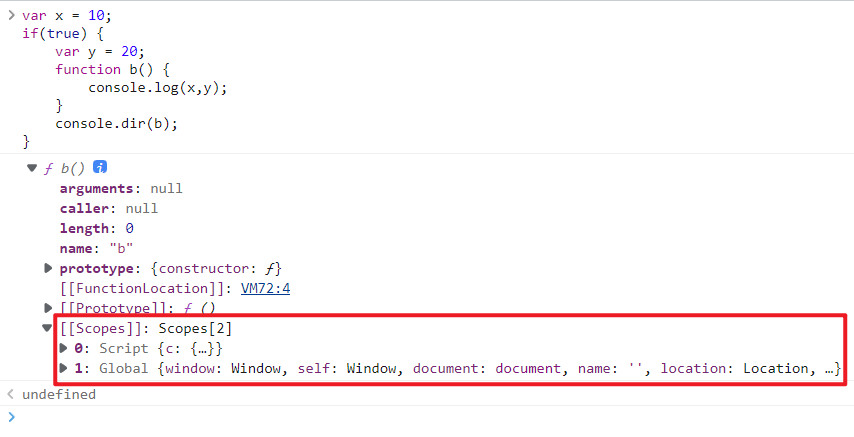
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 var x = 10 ;function a ( var y = 20 ; function b ( console .log (x,y); } return b; } a ()();
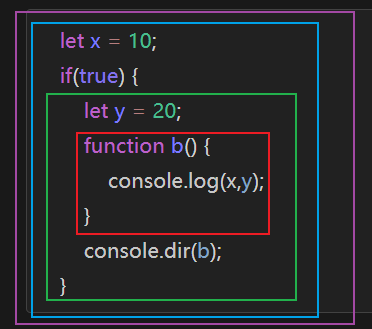
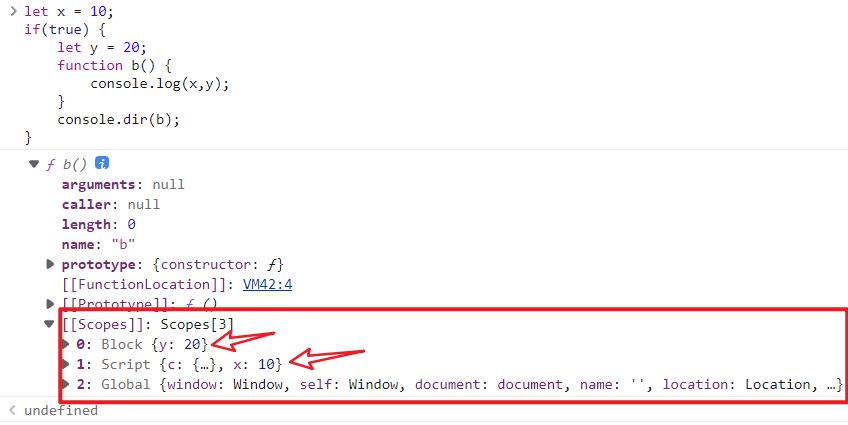
let,var 与作用域 1、如果函数外层引用的是 let 变量,那么外层普通的 {} 也会作为作用域边界,最外层的 let 也占一个 script 作用域
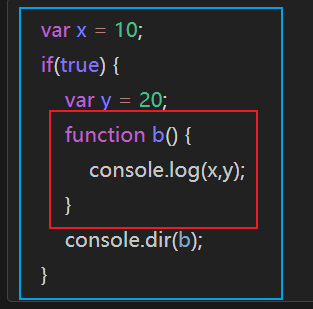
2、如果函数外层引用的是 var 变量,外层普通的 {} 不会视为边界
3、如果 var 变量出现了重名,则他俩会被视为同一作用域中的同一个变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 var e = 10 ; if (true ) { var e = 20 ; console .log (e); } console .log (e);
4、如果是 let,则视为两个作用域中的两个变量
1 2 3 4 5 6 let e = 10 ; if (true ) { let e = 20 ; console .log (e); } console .log (e);
Array 遍历数组
1 2 let fruits = {'Apple' ,'banana' };console .log (fruits.length );
通过索引访问数组元素
1 2 3 4 5 let first = fruits[0 ]let last = fruits[fruits.length - 1 ]
遍历数组
1 2 3 4 5 fruits.forEach (function (item, index, array ) { console .log (item, index) })
常见操作
方法
描述
push
添加元素到数组的末尾
pop
删除数组末尾的元素
shift
删除数组头部元素
unshift
添加元素到数组的头部
indexof
找出某个元素在数组中的索引
splice
通过索引删除某个元素
slice
复制一个数组
1 2 3 4 5 let arr = ['a' ,'b' ,'c' ];arr.join (); arr.join ('' ); arr.join ('-' );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 let arr = [1 ,2 ,3 ,6 ];function a (i ) { return i * 10 } arr.map ( i =>10 );
filter 例子
1 2 let arr = [1 ,2 ,3 ,6 ];arr.filter ( (i )=> i % 2 == 1 );
传给 filter 的函数,参数代表旧元素,返回 true 表示要留下的元素
forEach 例子
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 let arr = [1 ,2 ,3 ,6 ];arr.forEach ( (i ) => console .log (i) );
Object 语法 1 2 3 4 5 6 let obj = { 属性名: 值, 方法名函数, get 属性名 {}, set 属性名(新值) {} }
例1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 let stu = { name : "小明" , age : 18 , study : function ( console .log (this .name +"test" ); } }
例2:
1 2 3 4 5 6 let name = "小明" ;let age = 18 ;let study = function ( console .log (this .name +"test" ); } let stu = {name, age, study};
例3:注意,对象方法这么写,仅限于对象内部
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 let stu = { name : "小明" , age : 18 , study ( console .log (this .name +"test" ); } }
例4:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 let stu = { _name : null , get name () { return this ._name ; }, set name (name ) { this ._name = name; } }
调用set,get
1 2 stu.name = "小明" ; console .log (stu.name );
属性增删 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 let stu = {name : '小明' };stu.age = 18 ; delete stu.age ; stu.study = function ( console .log (this .name +"test" ); }
添加get,set
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 let stu = {_name : null };object.defineProperty (stu, "name" , { get ( return this ._name ; }, set (name ) { this ._name = name; } });
原型继承 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 let father = { f1 : '父属性' , m1 : function ( console .log ("父方法" ); } } let son = Object .create (father);console .log (son.f1 ); son.m1 ();
father 是父对象,son 去调用 .m1 或 .f1 时,自身对象没有,就到父对象找
son 自己可以添加自己的属性和方法
son 里有特殊属性 __proto__ 代表它的父对象,即为 son 的原型对象
基于函数的原型继承
函数职责
1、负责创建子对象,给予对象提供属性,方法,功能上相当于构造方法
2、函数存在一个特殊属性 prototype ,它就是函数创建的子对象的父对象。该属性的作用就是为新对象提供原型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function cons (f2 ) { this .f2 = f2; this .m2 = function ( console .log ("子方法" ); } } cons.prototype f1 = "父属性" ; cons.prototype m1 = function ( console .log ("父方法" ); }
配合new关键字,创建子对象
1 let son = new cons ("子属性" )
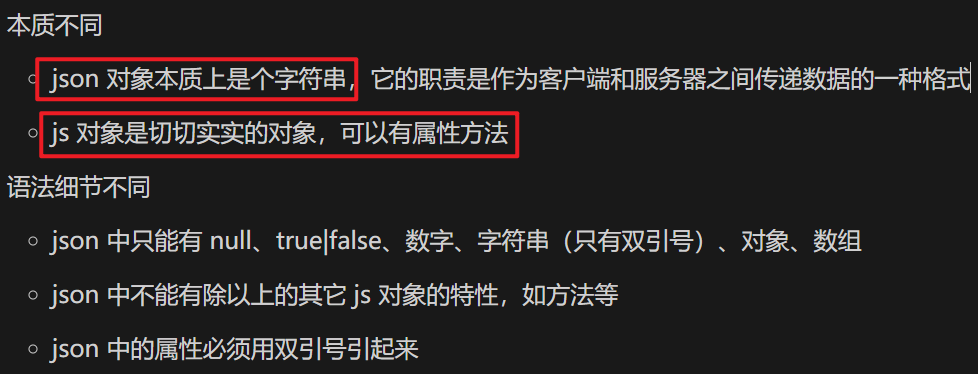
JSON json示例
1 2 3 4 { "name" : "张三" , "age" : 18 }
js对象示例
json 字符串与 js 对象的转换
1 2 JSON .parse (json字符串); JSON .stringify (js对象);
动态类型 js 属于动态类型语言,值有类型,但变量没有类型,赋值给变量时没要求
1 2 3 4 5 let a = 200 ;let b = 100 ;b = 'abc' ; b = true ;
动态类型看起来比较灵活,但变量没有类型,会给后期维护带来困难
1 2 3 function test (obj ) { }
展开语法 - JavaScript | MDN (mozilla.org)
易错点:
当传递给条件语句所有其他的值,包括所有对象会被计算为真
不要混淆原始的布尔值true和false 与 Boolean 对象的真和假
1 2 3 var b = new Boolean (false );if (b) if (b == true )
API 查找元素
document.getElementById:根据 id 值查找一个元素 document.querySelector:根据选择器查找第一个匹配元素 document.querySelectorAll:根据选择器查找所有匹配元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 <div > <div class ="title" > 学生列表</div > <div class ="thead" > <div class ="row bold" > <div class ="col" > 编号</div > <div class ="col" > 姓名</div > <div class ="col" > 性别</div > <div class ="col" > 年龄</div > </div > </div > <div class ="tbody" > <div class ="row" > <div class ="col" > 1</div > <div class ="col" > 张三</div > <div class ="col" > 男</div > <div class ="col" > 18</div > </div > </div > </div >
1 document .querySelector ('.title' );
1 document .querySelector ('.col' );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 document .querySelectorAll ('.col' );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 const thead = document .querySelector ('.thead' );thead.querySelectorAll ('.col' );
根据 id 属性查找的两种方法
1 2 document .getElementById ("id值" )document .querySelector ("#id值" )
修改元素内容
元素.innerHTML 元素.textContent
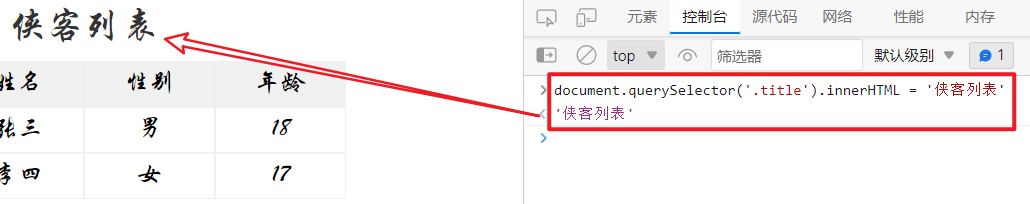
1 document .querySelector ('.title' ).innerHTML = '侠客列表'
使用元素.textContent这种方法也可以对元素内容进行修改,它们的区别是
innerHTML 会解析内容中的标签,textContext 不会解析内容中的标签
API注意:给 innerHTML 或 textContent 赋值空串,可以实现清空标签内容的效果
利用模板 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 <div > <div class ="title" > 学生列表</div > <div class ="thead" > <div class ="row bold" > <div class ="col" > 编号</div > <div class ="col" > 姓名</div > <div class ="col" > 性别</div > <div class ="col" > 年龄</div > </div > </div > <div class ="tbody" > </div > </div > <template id ="tp" > <div class ="row" > <div class ="col" > </div > <div class ="col" > </div > <div class ="col" > </div > <div class ="col" > </div > </div > </template > <script > let array = [ { id : 1 , name : '张三' , sex : '男' , age : 18 }, { id : 2 , name : '李四' , sex : '女' , age : 17 } ]; const tp = document .getElementById ("tp" ); const row = tp.content ; const [c1,c2,c3,c4] = row.querySelectorAll (".col" ); const tbody = document .querySelector (".tbody" ); for (const {id, name, sex, age} of array) { c1.textContent = id; c2.textContent = name; c3.textContent = sex; c4.textContent = age; const newNode = document .importNode (row, true ); tbody.appendChild (newNode); } </script >
Fetch API Fetch API 可以用来获取远程数据,它有两种方式接收结果,同步方式与异步方式
格式
同步方式
1 2 const 结果 = await Promise
await 关键字必须在一个标记了 async 的 function 内来使用
后续代码不会在结果返回前执行
异步方式
1 2 3 Promise .then (结果 => { ... })
在 express 服务器上有 students.json 文件
1 2 3 4 [ { "id" : 1 , "name" : "张三" , "sex" : "男" , "age" : 18 } , { "id" : 2 , "name" : "李四" , "sex" : "女" , "age" : 17 } ]
现在用 fetch api 获取这些数据,并展示
同步方式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 <script > async function findStudents ( try { const resp = await fetch ('students.json' ) const array = await resp.json (); const tp = document .getElementById ("tp" ); const row = tp.content ; const [c1,c2,c3,c4] = row.querySelectorAll (".col" ); const tbody = document .querySelector ('.tbody' ); for (const {id,name,sex,age} of array) { c1.textContent = id; c2.textContent = name; c3.textContent = sex; c4.textContent = age; const newRow = document .importNode (row, true ); tbody.appendChild (newRow); } } catch (e) { console .log (e); } } findStudents () </script >
fetch(‘students.json’) 内部会发送请求,但响应结果不能立刻返回,因此 await 就是等待响应结果返回
其中 resp.json() 也不是立刻能返回结果,它返回的也是 Promise 对象,也要配合 await 取结果
异步方式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <script > fetch ('students.json' ) .then ( resp =>json () ) .then ( array => const tp = document .getElementById ("tp" ); const row = tp.content ; const [c1,c2,c3,c4] = row.querySelectorAll (".col" ); const tbody = document .querySelector ('.tbody' ); for (const {id,name,sex,age} of array) { c1.textContent = id; c2.textContent = name; c3.textContent = sex; c4.textContent = age; const newRow = document .importNode (row, true ); tbody.appendChild (newRow); } }) .catch ( e =>console .log (e) ) </script >
第一个 then 是在响应返回后,才会调用它里面的箭头函数,箭头函数参数即 resp 响应对象
第二个 then 是在 json 解析完成后,才会调用它里面的箭头函数,箭头函数参数即解析结果(本例是 array 数组)
上一个 then 返回的是 Promise 对象时,才能链式调用下一个 then
Vue2 环境搭建
添加代理
DevServer | webpack
文本插值 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <template> <div> <h1>{{ name }}</h1> <h1>{{ age > 60 ? '老年' : '青年' }}</h1> </div> </template> <!-- template中只能有一个根元素 不能有多个 --> <script> const options = { data: function () { return {name: '张三', age: 18}; } }; export default options; </script>
属性绑定 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 <template> <div> <div><input type="text" v-bind:value="name"></div> <div><input type="date" v-bind:value="birthday"></div> <div><input type="text" :value="age"></div> </div> </template> <script> const options = { data: function () { return {name: '王五', birthday: '2003-03-30', age: 18}; } }; export default options; </script>
事件绑定 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 <template> <div> <div><input type="button" value="++单击事件" v-on:click="m1"></div> <br> <div><input type="button" value="--单击事件" @click="m2"></div> <br> <div>{{ count }}</div> </div> </template> <script> const options = { data: function () { return {count: 0}; }, methods: { m1() { this.count++; }, m2() { this.count--; } } }; export default options; </script>
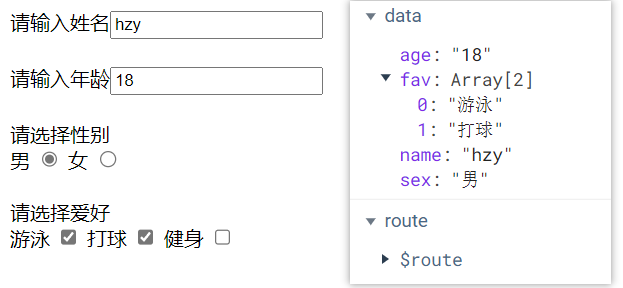
双向绑定 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 <template> <div> <div> <label for="">请输入姓名</label> <input type="text" v-model="name"> </div> <br> <div> <label for="">请输入年龄</label> <input type="text" v-model="age"> </div> <br> <div> <label for="">请选择性别</label> <br> 男 <input type="radio" value="男" v-model="sex"> 女 <input type="radio" value="女" v-model="sex"> </div> <br> <div> <label for="">请选择爱好</label> <br> 游泳 <input type="checkbox" value="游泳" v-model="fav"> 打球 <input type="checkbox" value="打球" v-model="fav"> 健身 <input type="checkbox" value="健身" v-model="fav"> </div> </div> </template> <script> const options = { data: function () { return {name: 'hzy', age: '18', sex: '男', fav: ['游泳', '打球']}; }, methods: {} }; export default options; </script>
计算属性
注意:如果通过普通的方法进行拼接,那么在每次调用该方法,都会重新加载一次。
如果使用computed进行拼接,那么在调用该方法后,会进行缓存,在下一次重复调用时,直接从缓存中获取
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 <template> <div> <h1>{{fullName}}</h1> </div> </template> <script> const options = { data: function () { return {firstname: '三', lastname: '张'}; }, // methods: { // fullName() { // return this.lastname + this.firstname; // } // }, computed: { fullName() { return this.lastname + this.firstname; } } }; export default options; </script>
vue-axios axios 它的底层是用了 XMLHttpRequest(xhr)方式发送请求和接收响应,xhr 相对于之前讲过的 fetch api 来说,功能更强大,但由于是比较老的 api,不支持 Promise, axios 对 xhr 进行了封装,使之支持 Promise,并提供了对请求、响应的统一拦截功能
安装
导入 :axios 默认导出一个对象,这里的 import 导入的就是它默认导出的对象
1 import axios from 'axios'
示例 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <template> <div> <input type="button" value="获取远程数据" v-on:click="sendRequest()"> </div> </template> <script> import axios from 'axios' const options = { methods: { async sendRequest() { const resp = await axios.get('/api/students'); console.log(resp); } } }; export default options; </script>
主要方法
请求
axios.get( url [, config])
axios.delete( url [, config])
axios.head( url [, config])
axios.options( url [, config])
axios.post( url [, data [, config]])
axios.put( url [, data [, config]])
axios.patch( url [, data [, config]])
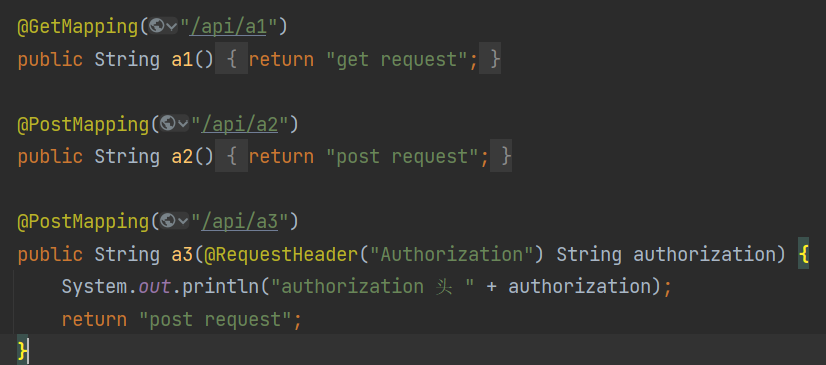
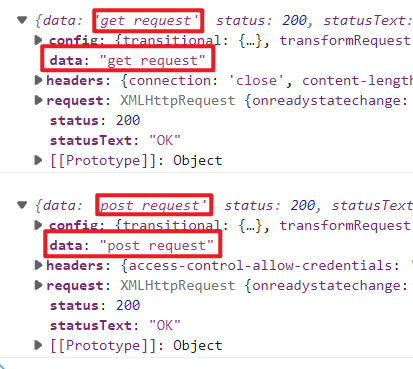
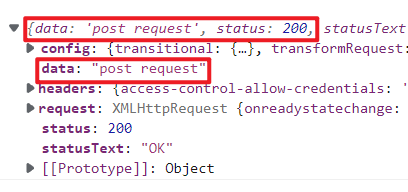
例1: 演示get请求,post请求和发送请求头
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 <template> <div> <input type="button" value="getRequest" v-on:click="sendRequest1()"> <input type="button" value="postRequest" v-on:click="sendRequest2()"> <input type="button" value="发送请求头" v-on:click="head()"> </div> </template> <script> import axios from 'axios' const options = { methods: { //1、演示get async sendRequest1() { const resp = await axios.get('/api/a1'); console.log(resp); }, //3、演示post async sendRequest2() { const resp = await axios.post('/api/a2'); console.log(resp); }, //3、发送请求头 async head() { const resp = await axios.post('/api/a3',{},{ headers: { Authorization: 'test' } }); console.log(resp); } } }; export default options; </script>
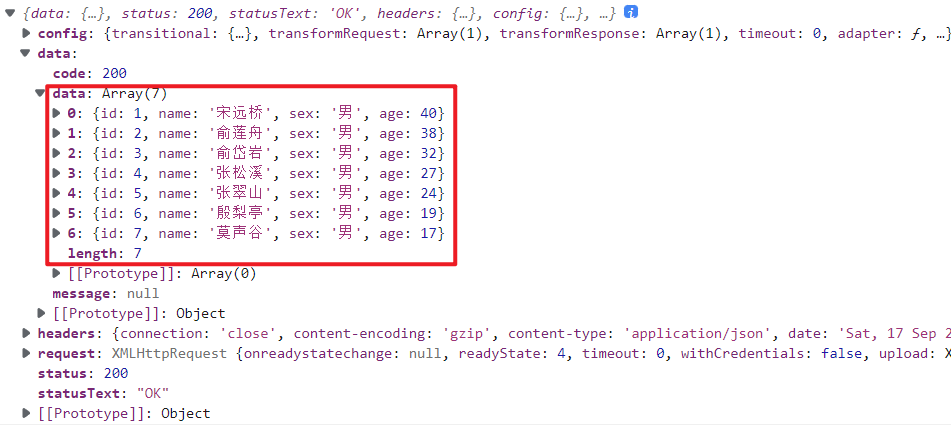
例2: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 <template> <div> <input type="button" value="获取远程数据-1" v-on:click="test1()"> <input type="button" value="获取远程数据-2" v-on:click="test2()"> <input type="button" value="获取远程数据-3" v-on:click="test3()"> <input type="button" value="获取远程数据-4" v-on:click="test4()"> </div> </template> <script> import axios from 'axios' const options = { methods: { //4、发送请求时携带查询参数 async test1() { const name = 'hzy'; const age = 18; const resp = await axios.post(`api/a4?name=${name}&age=${age}`); console.log(resp); }, //5.携带查询参数时带有特殊字符的处理方法 async test2() { const name = encodeURIComponent('&&&'); const age = 18; const resp = await axios.post(`api/a4?name=${name}&age=${age}`); console.log(resp); }, //6.将参数自动进行字符串的url编码并进行拼接 async test3() { const resp = await axios.post('api/a4',{},{ params: { name: '&&&', age: 20 } }); console.log(resp); }, //7.用请求体发送数据,格式为 urlencoded async test4() { const params = new URLSearchParams(); params.append("name","hzy"); params.append("age",24); const resp = await axios.post('api/a4',params); console.log(resp); }, //8.用请求体发送数据,格式为 multipart async test5() { const params = new FormData(); params.append("name","hzy"); params.append("age",24); const resp = await axios.post('api/a4',params); console.log(resp); }, //9.用请求体发送数据,格式为 json async test6() { const resp = await axios.post('api/a5json', { name: 'hzy', age: 50 }); console.log(resp); } } }; export default options; </script>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @GetMapping("/api/a1") public String a1 () { return "get request" ; } @PostMapping("/api/a2") public String a2 () { return "post request" ; } @PostMapping("/api/a3") public String a3 (@RequestHeader("Authorization") String authorization) { System.out.println("authorization 头 " + authorization); return "post request" ; } @PostMapping("/api/a4") public String a4 (String name, Integer age) { System.out.println("name: " + name + " age:" + age); return "post request" ; } @PostMapping("/api/a5") public String a5 (A5 a5) { System.out.println(a5); return "post request" ; } @PostMapping("/api/a5json") public String a5json (@RequestBody A5 a5) { System.out.println(a5); return "post request" ; }
默认配置 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 async test7 ( const _axios = axios.create ({}); const resp = await _axios.post ('api/a5json' , { name : 'hzy' , age : 50 }); console .log (resp); }
常见的 config 项
名称
含义
baseURL
将自动加在 url 前面
headers
请求头,类型为简单对象
params
跟在 URL 后的请求参数,类型为简单对象或 URLSearchParams
data
请求体,类型有简单对象、FormData、URLSearchParams、File 等
withCredentials
跨域时是否携带 Cookie 等凭证,默认为 false
responseType
响应类型,默认为 json
示例
生产环境希望 xhr 请求不走代理,可以用 baseURL 统一修改
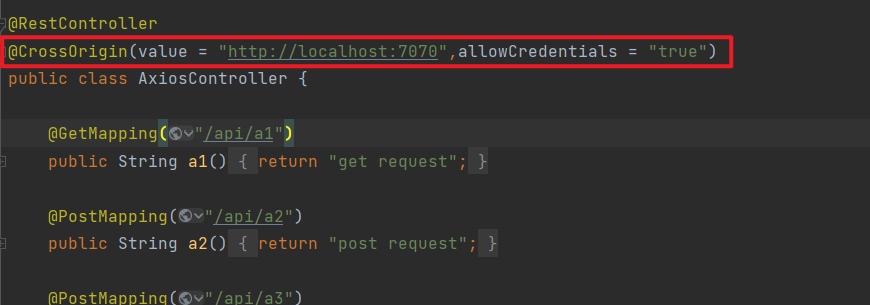
希望跨域请求携带 cookie,需要配置 withCredentials: true,服务器也要配置 allowCredentials = true,否则浏览器获取跨域返回的 cookie 时会报错
前端代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 async test7 ( const _axios = axios.create ({}); const resp = await _axios.post ('api/a5json' , { name : 'hzy' , age : 50 }); console .log (resp); }, async test8 ( const _axios = axios.create ({ baseURL : 'http://localhost:8080' , withCredentials : true }); const resp = await _axios.post ('api/a5json' , { name : 'hzy' , age : 50 }); console .log (resp); await _axios.post ('/api/a6set' ) await _axios.post ('/api/a6get' ) }, async test9 ( const _axios = axios.create ({ baseURL : 'http://localhost:8080' , withCredentials : true }); await _axios.post ('/api/a6set' ) await _axios.post ('/api/a6get' ) }
后端接口如下:
响应格式
名称
含义
data 响应体数据
status 状态码
headers 响应头
200 表示响应成功
400 请求数据不正确,如:age=abc
401 身份验证没通过
403 没有权限
404 资源不存在
405 不支持请求方式 post
500 服务器内部错误
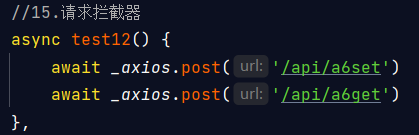
拦截器 请求拦截器 将_axios抽取到一个独立的js文件中
响应拦截器 条件渲染 列表渲染